Respiratory Booster - Tiger Milk Mushrooms
Respiratory Booster : Tiger Milk Mushrooms
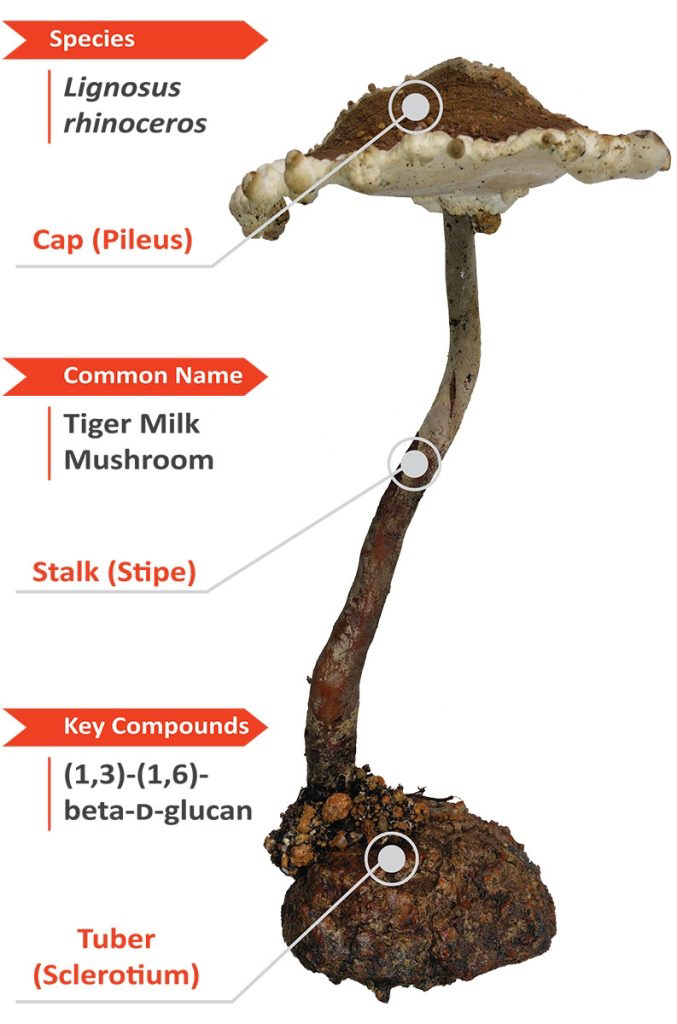
Tiger milk mushrooms has long been used as traditional medicines in South East Asia for various respiratory ailments.
Tiger milk mushroom (TMM) has been used as medicinal remedies for a long time in indigenous community of South East Asia region.
The name of Tiger milk mushroom came from the folklore that TMM grows in the area where the milk from tigress falls onto the ground when feeding to its cubs.
However, up until only the year of 2009, benefits of consuming TMM started to spread like wildfire after its cultivation was successful, making it commercially available.
Researches have shown that the use of TMM provides anti-inflammatory as well as anti-asthmatic properties. Consumption of TMM has lead to increment in the production of cytokine cells such as Immunoglobulin E (IgE) which helps to reduce allergic reaction.
Other than that, it was found that TMM has potent antioxidant and immunomodulatory properties which are beneficial to people with respiratory diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and bronchitis as well as post-Covid patients as TMM helps to reduce airway inflammation.
You may consider to give it a try if you're having chronic symptoms of respiratory problems.
References:
1. Tan, E.S.S., Leo, T.K. & Tan, C.K. (2021). Effect of tiger milk mushroom (Lignosus rhinocerus) supplementation on respiratory health, immunity and antioxidant status: an open-label prospective study. Sci Rep 11, 11781.
2. Nallathamby, N., Phan, C., Seow, S., Baskaran, A., Lakshmanan, H., Abd Malek, S. and Sabaratnam, V., (2018). A Status Review of the Bioactive Activities of Tiger Milk Mushroom Lignosus rhinocerotis (Cooke) Ryvarden. Frontiers in Pharmacology.
3. Johnathan, M., Gan, S. H., Ezumi, M. F. W., Faezahtul, A. H. & Nurul, A. A. (2016). Phytochemical profiles and inhibitory effects of Tiger Milk mushroom (Lignosus rhinocerus) extract on ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation in a rodent model of asthma. BMC Compl. Altern. Med. 16, 167.